source:
https://www.omicsonline.org/brain-signal-monitoring-and-encoding-for-humanoid-robots-use-2155-6210.1000e124.php?aid=20802taken from the Journal of Biosensors & BioelectronicsHumanoid robot is recognized as the best robotic type in robotic technology, which is required many components and related technologies for realistic implementations. Humanoid robotics has become the important issue of research and investigation in the world robotic society for years [1-3], where the main part of such robotic type components is the brain communication and commands. To obtain the realistic robotic brain and its functions, the brains signal and communications are required to manipulate, pattern and test [4-6], therefore, the searching of realized technique for brain signal monitoring and encoding remains. Basically, terahertz (THz) pulse generated by laser is the only one that can be used to probe and connect to the brain signals without damage, moreover, the brain signals can be modulated and demodulated by light via the THz carrier. However, there are applications, especially, in bioengineering, where THz signals have been involved in various works [7-9], especially, in medical applications [10,11]. In principle, THz is the term that applies to electromagnetic radiation with frequencies between the high-frequency edge of the millimeter wave band, 300 GHz (0.3 THz), and the low frequency edge of the far-infrared light band, 3,000 GHz (3THz). Corresponding wavelengths of radiation in this band range are from 1 mm to 0.1 mm (or 100 μm). Terahertz radiation is also called sub-millimeter radiation, terahertz waves, terahertz light, T-rays, T-waves, T-light, T-lux, or THz, consists of electromagnetic waves with frequency between 0.1 THz to 10 THz, and has widespread biomedical application involving the interaction of terahertz pulse with biological media [12-15]. Among them, terahertz radiation has been used successfully as a noninvasive imaging technique for detection of human skin cancer [16-18]. Recently, Yupapin and his colleagues have shown the interesting results of whispering gallery mode of light within a PANDA ring circuit [19-21], where the advantage is that the WGMs can be easily generated and controlled within the PANDA ring circuit, which is due to the nonlinear coupling effects introduced by the two side rings of the add-drop optical filter. Moreover, the WGM wavelength (frequency) and output power can be selected and controlled, which are useful for various applications.
In this article, the human brain signals are typically generated by the synapses, which can be coupled and communicated by the THz WGM signals, where the reflected signals are formed by the coupling signals between the suitable injected THz pulses and synapse signals, which can be detected by the external electronic instruments, and the synapse signals can be obtained by using the signal filtering device. The large volume brain signals can be probed and obtained by using the PANDA ring array, where each brain signal can be linked by the different WGM wavelengths, where finally, the different human mind commands can be monitored and recognized by the pattern recognitions, which are very useful for many applications.
In Figure 1, the WGMs within a PANDA ring can be easily obtained by using the commercial FDTD Opti-wave program, where the device parameters will be chosen closely to the practical device parameters. Here, the related equation and parameters are described and given in the reference list. The brain signal encoding model is as shown in Figure 2, where (a) neural linked by synapse, (b) brain signals, (c) large volume brain signal probing and encoding using PANDA ring circuit array network, where the THz WGM pulses can be generated and connected to the synapses by the thin film PANDA ring array system and electronic instruments.
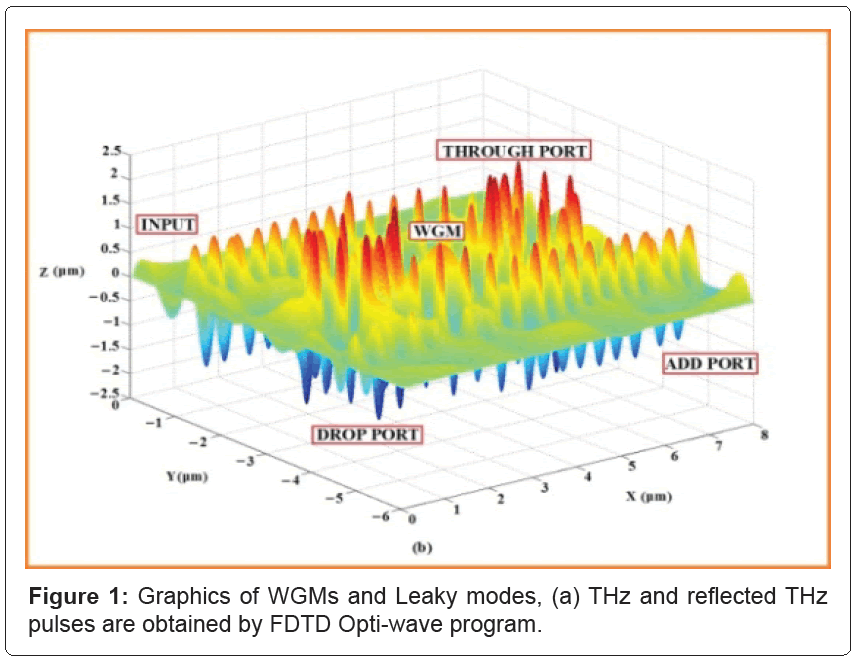 Figure 1
Figure 1: Graphics of WGMs and Leaky modes, (a) THz and reflected THz pulses are obtained by FDTD Opti-wave program.
 Figure 2
Figure 2: Brain signal encoding model, where (a) neural linked by synapse (b) brain signals (c) large volume brain signal probing and encoding using PANDA ring circuit array network [22].
To form the coupling output of synapse and THz WGM signals, in this study the synapse signal is modeled as an electrical pulse, which can be coupled and modulated into the PANDA ring circuit by the THz WGMs, where the reflected WGM signals are obtained via the WGM signal direct detection or the drop port output signals, in which the different synapses and WGMs signals can be distinguished by using the filtering devices, where the variables such as wavelengths (frequencies), signal amplitudes and signal forms are the calculation and interpretation parameters.
We have described the use of THz WGM within the PANDA ring circuit for humanoid robot pattern recognitions, where the coupling signals between THz WGMs and brain signals can be probed and formed the human mind encoded signals (pattern recognitions). The WGM is generated by the PANDA ring circuit, which is within the THz frequency regime. After coupling, the reflected WGM signals are the moderated signals, where the synapse signals are merged within the WGM carrier signals. The required synapse signals can be probed and filtered to form the human mind and establish the encoded commands.
The large volume of brain signals can also be probed by using the PANDA ring circuit array, where the different frequency output signals can be obtained for large volume brain cells, i.e. commands. In applications, this method can be used to form the humanoid robotics, where the human mind functions can operate to the required destinations i.e. organs faster than typical operation via the direct link, which is required to transfer human mind computer commands to the humanoid robots. Apart from computer communications, such a proposed technique can also be useful for other brain signal monitoring and detecting applications, for instance, medical diagnosis and therapy, dream and sleeping investigation, blind and disable people communication, psychiatric and crime suspect investigations.